


By : chef ssentongo Geoffrey
From : Mr Easy Recipes
The terms leader, manager, and operator describe distinct roles in an organization, each with different focuses and responsibilities. Here’s a breakdown of their key differences:
1. Leader

- Focus: Vision, inspiration, and long-term direction.
- Key Traits: Charismatic, strategic, innovative, motivational.
- Responsibilities:
- Sets the vision and mission of the organization.
- Inspires and influences people to follow a shared goal.
- Encourages innovation and change.
- Builds culture and empowers teams.
- Example: A CEO or founder who defines the company’s future.
2. Manager

- Focus: Execution, organization, and efficiency.
- Key Traits: Structured, detail-oriented, goal-driven.
- Responsibilities:
- Plans, coordinates, and oversees day-to-day operations.
- Allocates resources and sets short-term objectives.
- Monitors performance and ensures targets are met.
- Solves problems and maintains team productivity.
- Example: A department head ensuring projects are completed on time.
3. Operator

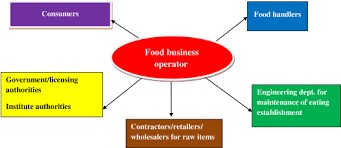
- Focus: Tactical execution and hands-on work.
- Key Traits: Practical, process-driven, specialized.
- Responsibilities:
- Handles the actual implementation of tasks (e.g., production, logistics, IT).
- Follows established procedures to deliver results.
- Works within defined systems with measurable outputs.
- Often more technical or specialized than managers.
- Example: A factory supervisor, software engineer, or supply chain analyst.
Key Differences at a Glance

Aspect Leader Manager Operator Focus Vision & inspiration Planning & coordination Execution & processes Timeframe Long-term Medium-term Short-term Skills Emotional intelligence Organizational skills Technical proficiency Output Direction & culture Efficiency & results Deliverables & output
Overlap & Collaboration
- A great manager often has leadership qualities.
- An effective operator may need managerial skills.
- Strong leaders ensure managers and operators align with the vision.
In summary:
- Leaders set the why and where.
- Managers define the how and when.
- Operators handle the what and doing.
Would you like examples from a specific industry?
Leave a comment